paired end sequencing wikipedia
End-sequence profiling ESP sometimes Paired-end mapping PEM is a method based on sequence-tagged connectors developed to facilitate de novo genome sequencing to identify high-resolution copy number and structural aberrations such as inversions and translocations. Combining data from mate pair sequencing with those from short-insert paired-end reads provides increased information for maximising sequencing coverage across a genome 1.
In single-end reading the sequencer reads a fragment from only one end to the other generating the sequence of base pairs.

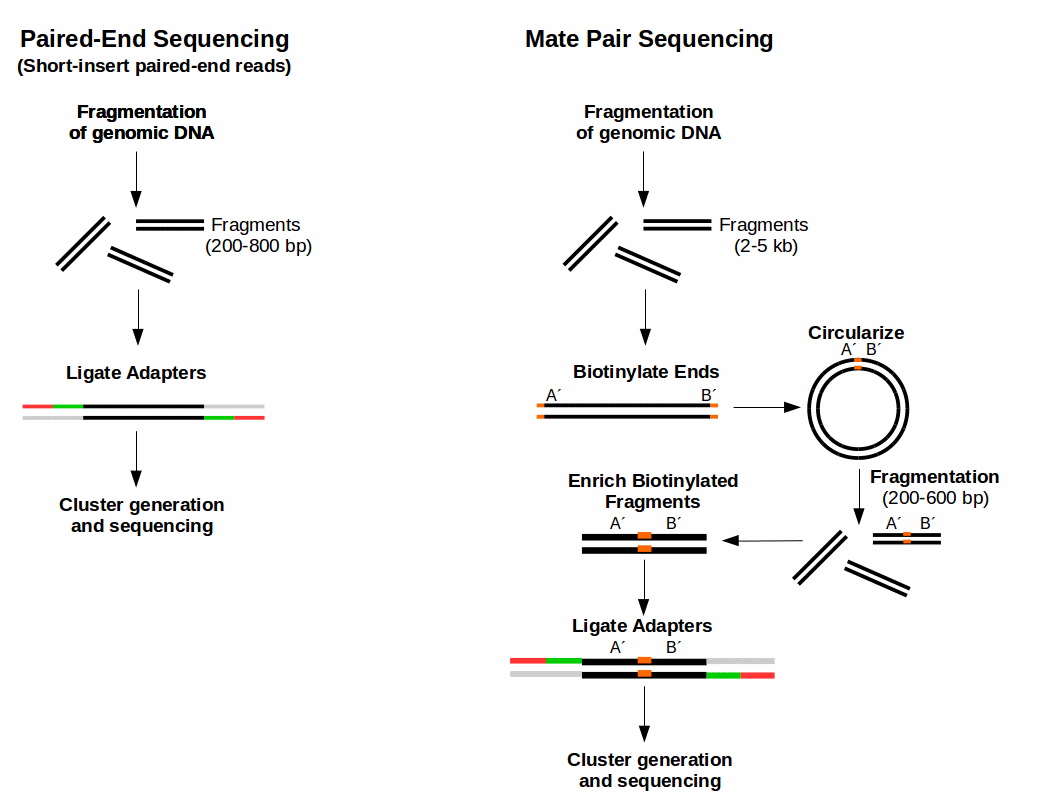
. Mate pair sequencing involves generating long-insert paired-end DNA libraries useful for a number of sequencing applications including. Fast and Accurate Next-Generation Sequencing Results Enabled by Ion Torrent Technology. In addition to producing twice the number of reads for the same time and effort in library.
Paired-end sequencing facilitates detection of genomic rearrangements and repetitive sequence elements as well as gene fusions and novel transcripts. The larger inserts mate pairs can pair reads across greater distances. Fold change 15 FDR 005 P-value 005 and Test status OK is one criteria which was taken but I have also seen people.
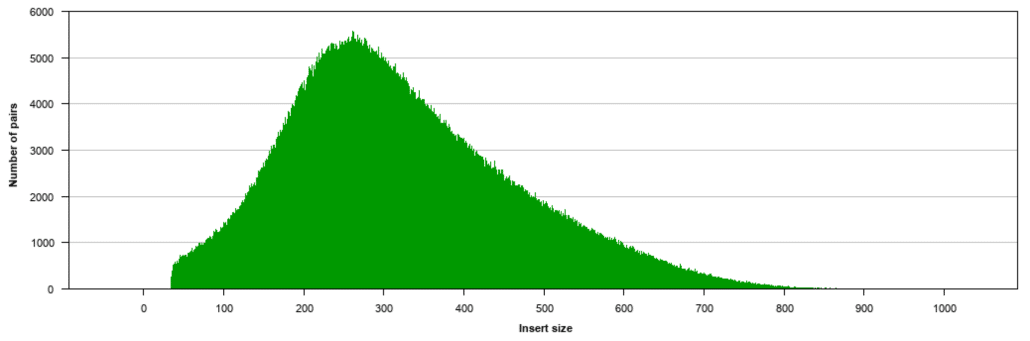
Paired end sequencing refers to the fact that the fragment s sequenced were sequenced from both ends and not just the one as was true for first generation sequencing. The figure shows the workflow for mate-pair library preparation for Illumina sequencing. The preparation of mate pair libraries is designed to allow classical paired-end sequencing of both ends of a fragment with an original size of several kilobases.
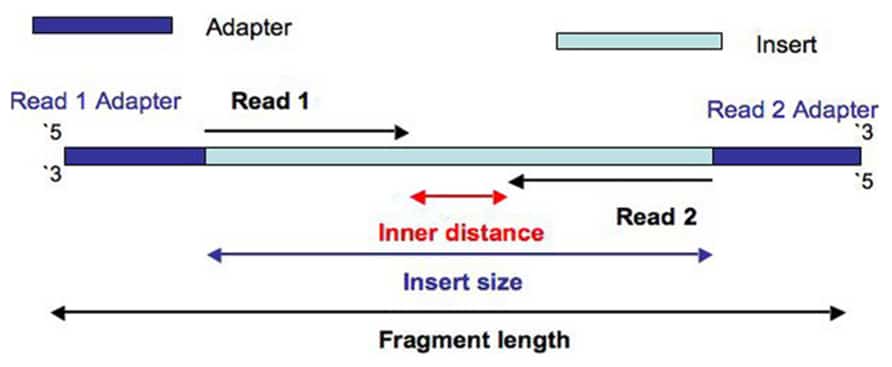
Read 1 often called the forward read extends from the Read 1 Adapter in the 5 3 direction towards Read 2 along the forward DNA strand. Combining data generated from mate pair library sequencing with that from short-insert paired-end reads provides a powerful combination of read lengths for maximal sequencing coverage across the genome. Some of these technologies emerged between 1994 and 1998 and have been commercially available since 2005.
There is a unique adapter sequence on both ends of the paired-end read labeled Read 1 Adapter and Read 2 Adapter. Sequencing information from paired-end reads play an important role in Illuminas technology by increasing the output from a sequencing run identifying splice variants in RNA-seq and to deduplicate remove duplicate copy reads. Described below are two of the most prominent in situ Hi-C.
Ad Enable a Range of Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Applications wSpeed and Scalability. In paired-end reading it starts at one read finishes this direction at the specified read length and then starts another round of. Here are the reads.
Six with physical mapping data that anchor scaffolds to chromosome locations 13 with paired-end RNA sequencing RNAseq data and three with new assemblies based on re-scaffolding or Pacific Biosciences. Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing. The implementation of paired-end or mate-paired reads in massively parallel sequencing which are sequence reads from both ends of longer DNA molecules of known length permits the analysis of genomic fragments up to 510 Kb in length depending on the platform.
Pairs come from the ends of the same DNA strand The differences between PE and MP reads include. It also requires an extremely high sequencing depth of around 5 billion paired-end reads per sample to achieve the resolution of data described by Rao et al. Therefore they are able to better cover highly.
Briefly the target genomic DNA is isolated and partially digested with restrictio. As sequencing projects began to take on longer and more complicated DNA sequences multiple groups began to realize that useful information could be obtained by sequencing both ends of a fragment of DNA. Learn about the difference between Paired-End and Single-Run sequencing and why the former creates more precise alignments than the latter especiall.
Broader application benefited from pairwise end sequencing known colloquially as double-barrel shotgun sequencing. For your De novo genome assembly Fig. The second sequence is a shorter duplicate of the first sequence.
These reads are assumed to be identical to. In almost all cases short paired-end reads trump single-end reads that sequence approximately the same number of bases. Paired-end sequencing facilitates detection of genomic.
Library preparation protocols -- In short PE protocols attach an adapter SP1 to the fwd end and another adapter SP2 to the reverse end. For subsets of the assemblies we integrated these with additional supporting data to confirm and complement the synteny-based adjacencies. This can be very helpful e.
In conventional paired-end sequencing you simply sequence using the adapter for one end and then once youre done you start over sequencing using the adapter for the other end. The first sequencing step is started by targeting SP1 to generate the forward read. Since the beginning of 2013 this preparation has been based on Nextera.
The present invention provides for a method of preparing a target nucleic acid fragments to produce a smaller nucleic acid which comprises the two ends of the target nucleic acid. Paired-end sequencing allows users to sequence both ends of a fragment and generate high-quality alignable sequence data. Typical experimental design advice for expression analyses using RNA-seq generally assumes that single-end reads provide robust gene-level expression estimates in a.
Its a subset of the first sequence starting 200 bp downstream of the first. The idea is to have one of the paired-end reads mapping uniquely to the first 200 bp of the first sequence and the other read mapping to the duplicated region. Short paired-end reads provide an additional benefit in that they can identify a large fraction of differentially expressed isoforms for the cost of gene-level analysis with longer single-end reads.
These fragments are. Several techniques that have adapted the concept of in situ Hi-C exist including Sis Hi-C OCEAN-C and in situ capture Hi-C. What is the safe fold change to consider in a RNA-seq experiment.
Specifically the invention provides cloning and DNA manipulation strategies to isolate the two ends of a large target nucleic acid into a single small DNA construct for rapid cloning. Paired-end sequencing allows users to sequence both ends of a fragment and generate high-quality alignable sequence data. This means your two reads are the reverse complement of the 100 3-most bases of the Watson strand and the Crick strand.
It is also called next-generation sequencing or second-generation sequencing. Read 2 often called the reverse read extends from the Read 2 Adapter in the 5 3 direction.

Hi C Genomic Analysis Technique Wikipedia

File Chromosome Conformation Techniques Jpg Wikipedia

Bacterial Chromosome Replication Biology Lessons Chromosome Biology
What Are Paired End Reads The Sequencing Center
What Are Paired End Reads The Sequencing Center
Pathogens Free Full Text Hpv Deepseq An Ultra Fast Method Of Ngs Data Analysis And Visualization Using Automated Workflows And A Customized Papillomavirus Database In Clc Genomics Workbench Html
Plos Computational Biology Informatics For Rna Sequencing A Web Resource For Analysis On The Cloud
What Is Mate Pair Sequencing For
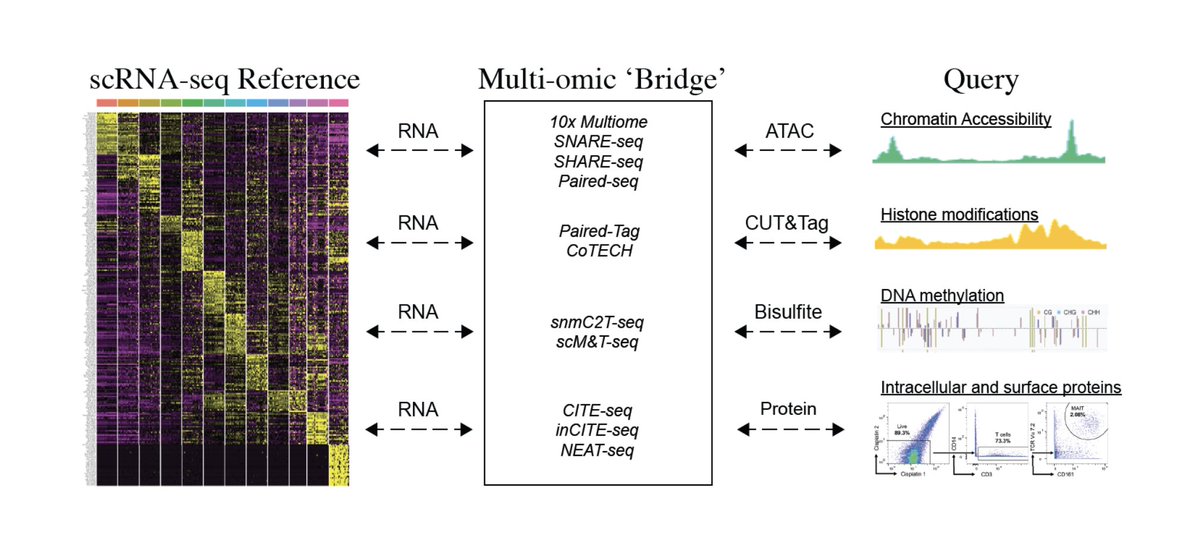
Rahul Satija Satijalab Twitter

What Is The Difference Between Single End And Paired End In Sequencing
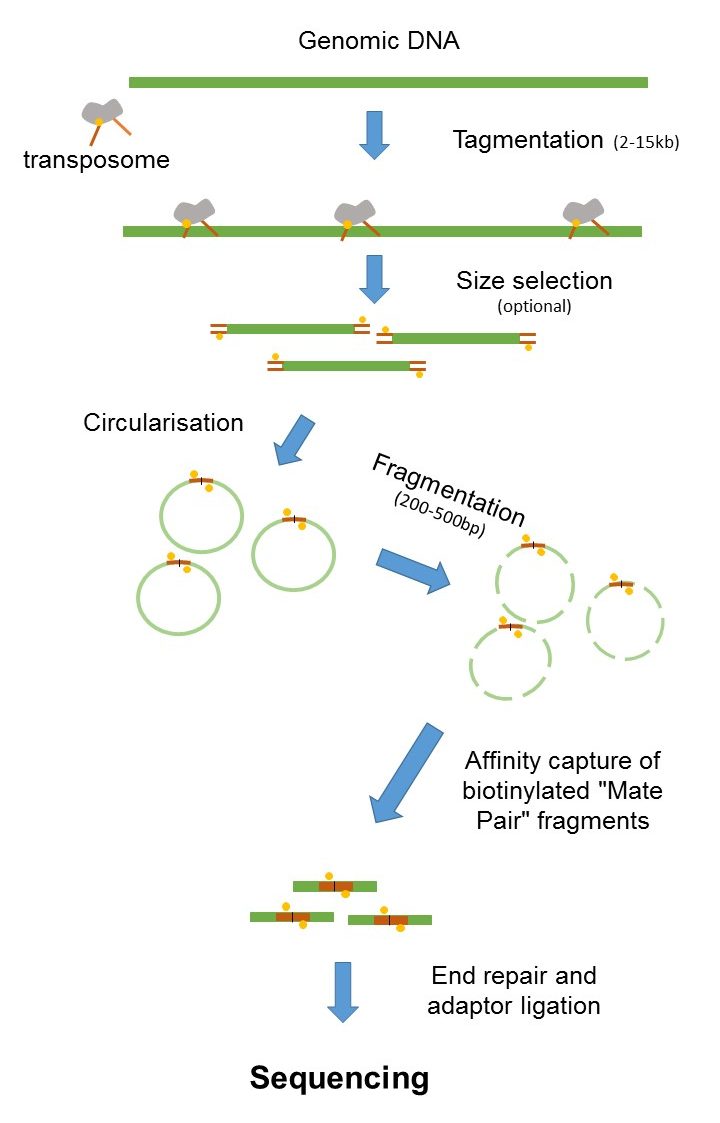
Mate Pair Sequencing France Genomique

Rna Seq Basics Applications And Protocol Technology Networks
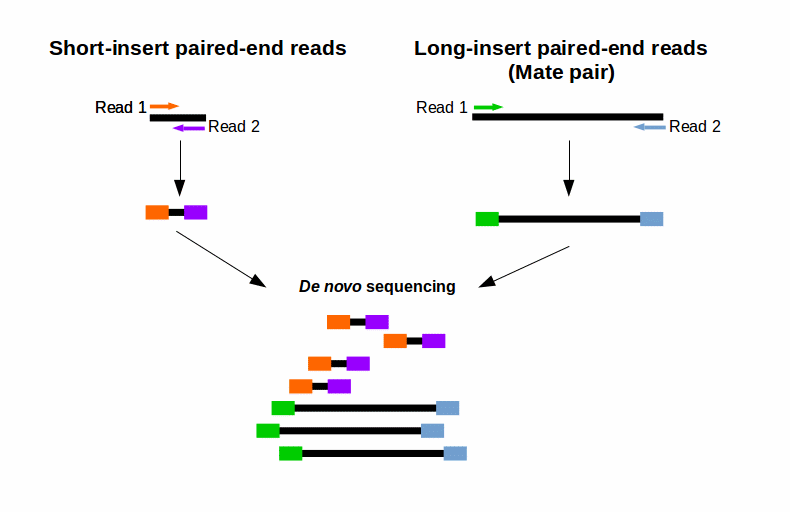
What Is Mate Pair Sequencing For
Whole Genome Sequence Analysis Of Salmonella Typhi In Papua New Guinea Reveals An Established Population Of Genotype 2 1 7 Sensitive To Antimicrobials Plos Neglected Tropical Diseases

Bacterial Chromosome Replication Biology Lessons Chromosome Biology

Paired End Shotgun Sequencing Okinawa Institute Of Science And Technology Graduate University Oist



